ITI Methodology
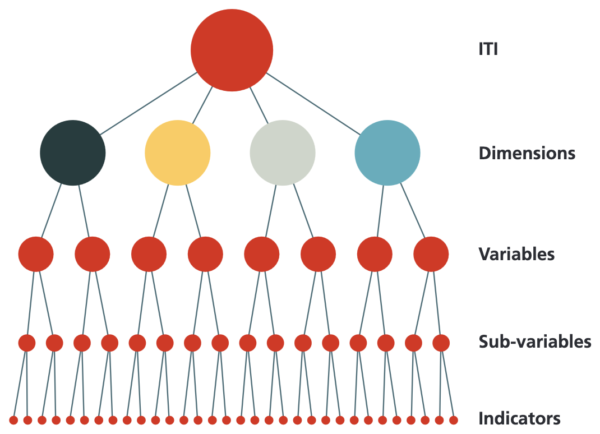
The Infrastructure Transparency Index (ITI) is an instrument of CoST -the Infrastructure Transparency Initiative that draws on four building blocks known as dimensions, namely: enabling environment, capacities and processes, citizen participation, and data publication.
The enabling environment evaluates the national or sub-national context with its legal framework. The indicators in the first dimension are evaluated using information that is available on official websites containing national regulatory frameworks, and information focused on transparency, public procurement, public infrastructure and public finances.
The capacities and processes evaluates procuring entities developing public infrastructure, assessing their procedures and capabilities for managing and disclosing information. The citizen participation measures the opportunities for inclusive public engagement through the project’s life cycle, and how effectively citizens are using the disclosed information. The indicators from these two dimensions are evaluated using information that is captured from a survey that has to be undertaken by a selected government officer at each selected entity.
Objectives and Outcomes
The ITI aims to:
Principles
The ITI was designed and developed to comply with these principles:
And its implementation process is structured to follow these other principles:
Implementation
The ITI is designed to be implemented at a national or sub-national scale. This means that the implementation coverage is flexible. For example, one country, one province or state can decide to implement it without requiring other countries, provinces or states to participate in the process. Or well, a regional implementation can be conducted to assess a group of countries, provinces or states in one the same process.
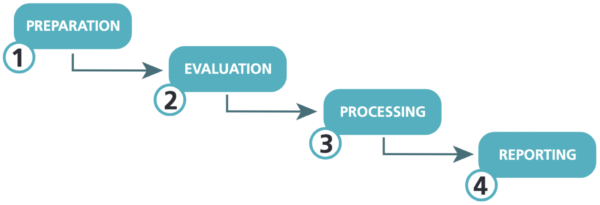
- The preparation stage involves working and defining several aspects to enable and facilitate the data collection. For example, to set an evaluation team, to train the team, to get and adapt materials such as templates and data processing worksheets, to define the period of study, to define the entities and projects to be evaluated, and to conduct key preparation events, such as kickoff meetings and webinars.
- Later, the required data is collected in the evaluation stage. The ITI uses two different methods to do this, desktop research and an entity survey. The two dimensions evaluated by desktop research include two or three different data reviews, and the two dimensions evaluated with the survey require specific evidence and endorsement from the entities, as well as its own data review process.
- During the data processing stage, the collected data is converted to scores in the range zero to one hundred (0−100) for each indicator, sub-variable, variable and dimension, based on their assessment and weightings. All ITI components have associated differentiated weightings according to their relative importance.
- Finally, the reporting stage involves the preparation, publication and public presentation of ITI results. The stage also involves follow-up meetings, training, or other forms of support to stakeholders. In this final stage it is important to set commitments at the centralised and decentralised levels to promote transparency and accountability as means to improve management of public infrastructure for the common good.
Detailed information about the methodology and implementation process is available in the ITI Manual.